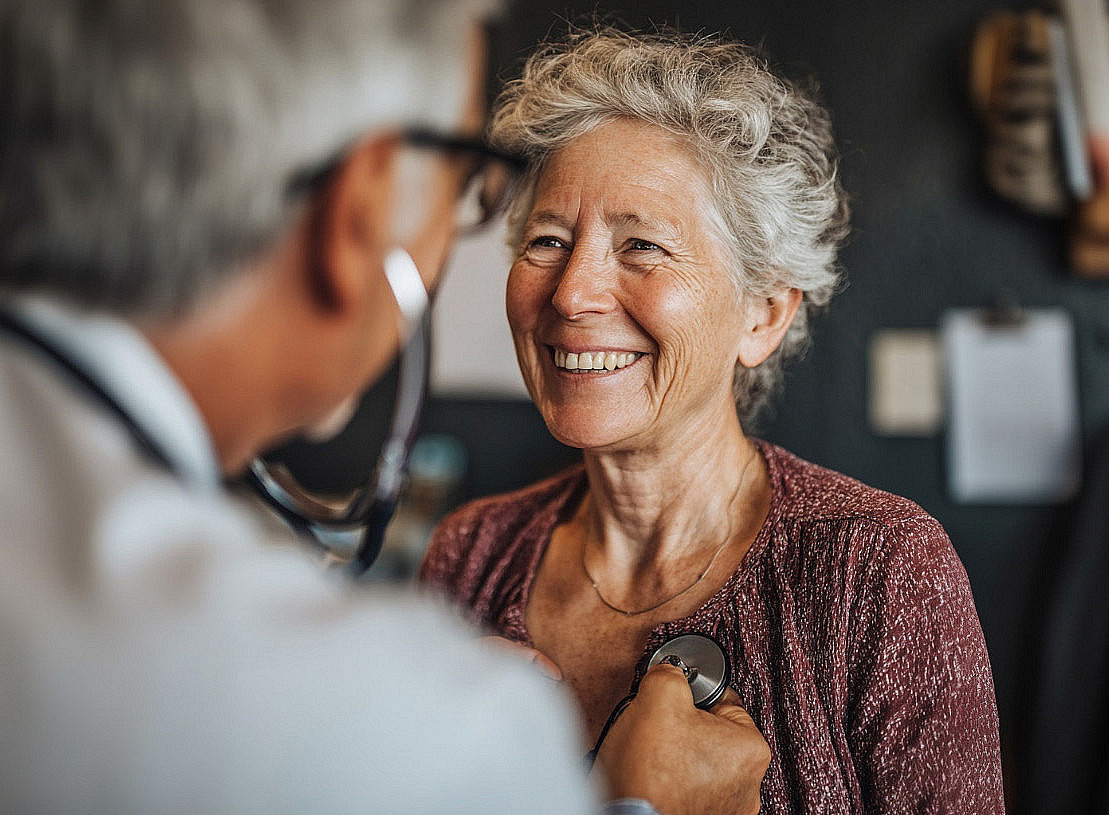
Young adults between the ages of 18 and 35 and seniors aged 60 to over 90 can participate, provided they have no serious pre-existing conditions or metallic implants. Participants receive a head-to-toe check-up, including whole-body magnetic resonance imaging, liver ultrasound, and blood, urine, stool, mucous membrane, and hair tests. Their eyes, blood sugar, body fat, and physical and mental fitness will also be closely examined. These examinations will be carried out every three years on two to three half-day appointments and are planned to continue until 2034. The participants receive financial compensation for their time. The results of the study will contribute to the development of new nutritional strategies, fasting methods, and medications that will keep us healthy for longer.
The study is being conducted by the MetAGE Cluster of Excellence, an association of scientists from the University of Graz, the Medical University of Graz, the Medical University of Vienna, and Joanneum Research. The cluster, which is funded by the Austrian Science Fund FWF, the province of Styria, and the city of Graz, also operates the newly established Center for Healthy Aging in Graz. This is where the research for the “Pro-MetAGE” study is also being conducted.
Further information & pre-registration: https://metage.at/en/contact-study-participation